Biomedical research has given us many alternatives to keep our body balanced. These alternatives tend to favour the organic production of the chemical compounds that are necessary to keep us healthy. One of the most popular suggestions today is to encourage the production of melatonin.
Melatonin has important benefits to sleep or to control stress and weight gain. In this article, we are going to explain what melatonin is, what it is for, how to take it, what foods contain melatonin, and its side effects.
What is melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone synthesized by an organic molecule called tryptophan. This molecule is obtained directly from the daily diet, that is to say, it is an essential amino acid for our organism, in addition to being a primary source of proteins.
It has been studied since the beginning of the past century, and its scientific name is N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine. It is produced in the pineal gland, located in the center of the brain of vertebrates, and has significant effects on the regulation of various neurological and physiological processes, such as sleep and cell oxidation.
This hormone is present both in human beings and animals, plants and some fungi. In the case of human beings, melatonin is synthesized continuously, although the rhythm usually slows down after the age of 30.
In addition, both internal and external factors favor or hinder the release of melatonin, for example, climate or stress. This can be compensated by a diet rich in foods that promote melatonin synthesis, such as oats, cherries, corn, tomatoes, potatoes, rice, nuts or plums.
Melatonin benefits
Melatonin has a lot of properties and benefits. For instance, it is said to have positive effects in the prevention of migraines, in the treatment of some carcinogenic tumours, in the protection of neurons and brain tissue, in the management of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's dementia and even favour the regulation of the menstrual cycle and menopause.
In addition, melatonin has been studied in relation to cardiovascular diseases and people with depression and bipolar disorder diagnosis. However, its best-known benefits are sleeping improvement, weight control and the slowing down of cellular aging.
1. Melatonin for sleep
It is produced by the pineal gland, so melatonin is essential to control circadian rhythms, this is, the changes that take place in our organism according to the related cycles, such as light and darkness.
This hormone participates importantly in the regulation of the sleep cycle: it helps the body to synchronize with environmental cycles and regulates the time it takes to fall asleep.
Melatonin is inhibited by the light, and it is stimulated by darkness, so its levels and effects usually increase at night. This is the reason why many people recommend taking melatonin for sleep.
2. To prevent weight gain
The prevention of weight gain is one of the most studied benefits of melatonin recently. It has been discovered that taking melatonin favors a molecular mechanism that burns body fat, so it's credited with being an anti-obesity hormone.
In recent research carried out with mice by scientists from La Paz-Carlos III Hospital in Madrid and The University of Texas Health Science Center, it is said that the regular consumption of melatonin has significant effects on the burning of calories and therefore on the prevention of weight gain.
Moreover, the same study says that the consumption of melatonin and the consequent reduction of fatty adipose tissue (the primary source of fat, which is dangerous in excess), was independent of the diet or physical activity of the mice, so it could be one of the new tools to fight obesity.

3. To prevent aging
Our organism metabolizes oxygen continuously, which triggers cell oxidation and aging. This is especially true when you exercise intensely on a regular basis, but it can also happen with everyday activities.
Melatonin is a hormone that protects cells from pro-oxidants because it helps to purify the excess of oxygen that we metabolize. It also regulates the enzymes that also have antioxidant properties without reducing the number of cells in the tissues.
On the other hand, melatonin has neuroprotector effects because it spreads easily throughout the body; it is also able to cross the blood-brain barrier. Consequently, this hormone protects the cell membrane from oxidative damage, which helps prevent aging.
4. To help with jet lag
Substantial scientific evidence supports the idea that melatonin can improve significantly some jet lag symptoms such as alertness or lack of sleep.
How to take melatonin
As we will explain later, melatonin is found in many foods we eat on a daily basis. However, there are also melatonin pills or drops that serve as food supplements, and even in creams or capsules.
Recommended melatonin dosage
The recommended dosage of melatonin is between 1 and 3 milligrams a day, although you can also find 5-milligram pills. Above all, it must be consumed taking into account its effects on circadian rhythms.
It is recommended to take at night because taking it during the day could be counterproductive in the regulation of the sleep cycle.
Where to buy melatonin
This hormone can be purchased in chemists without a prescription and in supermarkets. The dosage and the price vary depending on the product, but it goes from 7.5 to 15 dollars.
You can also find this product in the format of drops. In this case, the price is a bit higher than the one of the pills: from 10 to 21 dollars.
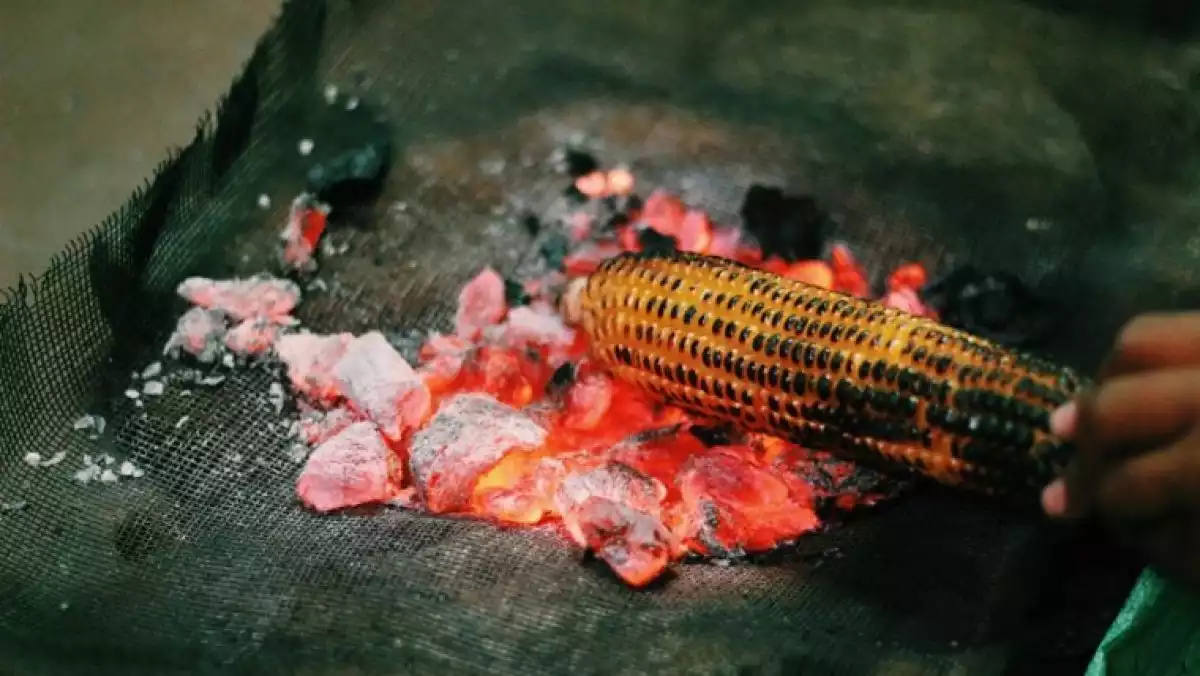

What foods contain melatonin?
Among the foods that have melatonin and that we can consume on a daily basis are the rice, oats, corn, tomatoes, and bananas.
1. Rice
Rice is a very nutritious food because it contains a lot of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals, apart from melatonin.
2. Oats
Although the amount of melatonin present in oats is not very high, this cereal is a very recommended food because it also contains a lot of minerals, vitamins and dietary fiber.
3. Corn
Corn, like rice, has been a very important food in some diets. A corn cob provides between 60 and 150mg of melatonin, in addition to carbohydrates and minerals.
4. Tomato
Tomatoes contain a modest but significant amount of melatonin. However, its antioxidant properties make it a very beneficial healthy food.
5. Banana
Apart from melatonin, bananas provide our body with a lot of potassium, and in consequence, they improve cardiovascular health, thus contributing to the prevention of heart accidents and other circulation-related problems.
Melatonin side effects and contraindications
As it is a natural hormone, no cases of intoxication or overdose due to melatonin supplementation have been reported.
However, it is important to take precautions in the case of babies, children and during pregnancy and breastfeeding periods, as well as to verify the right dosage during the treatment of depression, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Although melatonin taken orally is usually safe, some side effects may occur such as a headache, dizziness, nausea, and drowsiness.
Moreover, other side effects are less common such as the temporary feeling of depression, shivers and/or cramps, irritability, confusion and low blood pressure.
As for possible drug interactions, melatonin is not recommended for people who are being treated with the following drugs:
Anticoagulants and medicines or herbs that reduce blood clotting.
Anticonvulsants
Medication for blood pressure
Central nervous system depressants
Medication for diabetes
Contraceptive pills and treatments
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as fluvoxamine.
Immunosuppressive drugs