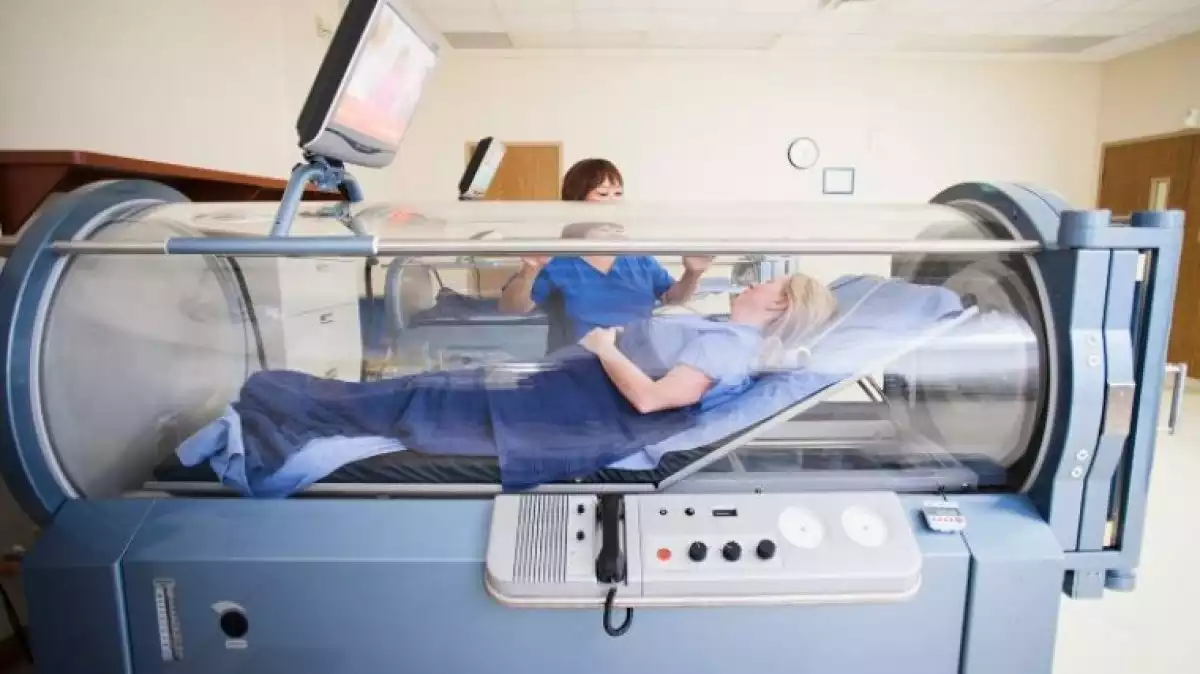
In general, oxygen therapy is a type of medical treatment that uses the application of oxygen using different oxygen supply devices to cure or manage different conditions such as acute asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
If you want to know more about this medical technique, in this article, we are going to tell you what oxygen therapy is, what benefits it has and which devices are used to carry out the treatment.
What is oxygen therapy?
Oxygen therapy consists of the voluntary administration of oxygen at higher concentrations than those of ambient air. This practice is used to treat or prevent different pathologies and conditions such as those described below:
Hypoxemia (lack of oxygen in the blood)
Severe shortness of breath (acute asthma or pneumonia, for instance)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, which includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and chronic asthma)
Pulmonary hypertension
Heart attack
Short-term therapy, such as post-anesthesia recovery
Air gangrene and embolism
Decompression discomfort
Carbon monoxide poisoning
Cerebral hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the brain)
Oxygen therapy is also known as a series of different techniques in which oxygen, ozone, or hydrogen peroxide are administered through gas or water to kill microorganisms, improve cell function, and promote healing of damaged tissues.
In general, breathing prescribed oxygen increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, reduces extra work for the heart, and decreases breathing difficulty. Oxygen therapy is often recommended both at home and in hospitals.
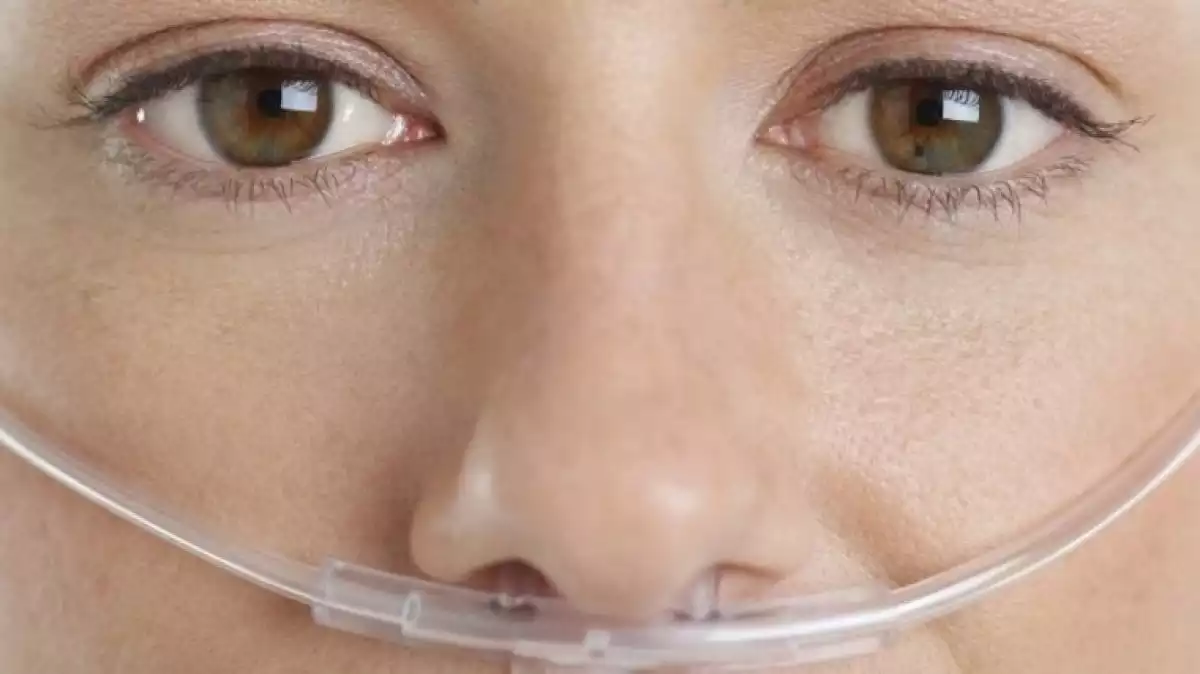
Oxygen therapy benefits
Oxygen therapy consists of a key treatment for respiratory care. Its primary purpose is to increase the oxygen saturation in tissues where the levels of concentration are too low due to some pathology or condition. However, other added benefits have also been described, such as those in the following list:
Improves the production of white blood cells.
Improves oxygen delivery from the bloodstream to body tissues.
Accelerates petrochemical decomposition.
Increases the effectiveness of antioxidant enzymes.
Increases flexibility and efficiency of red blood cell membranes
Accelerates the cycle of citric acid, which in turn stimulates the body's metabolism
Oxygen facial therapy
On the other hand, oxygen facial therapy is an aesthetic treatment used to rejuvenate the skin on the face and neck. It consists of activating the blood circulation and apply oxygen directly to the skin to stimulate the production of collagen, elastin and other nutrients, to promote skin hydration and thus delay aging. It is a painless technique that is carried out with a facial ultrasound device.
Besides delaying aging, the oxygen facial also leaves skin luminous, elastic, without flaccidity and it fights spots, acne, and scars. In general, it is usually recommended for people over 35 years old and often, to have some effect, people need 6 to 10 sessions (always depending on the individual case of the person, age and facial condition).
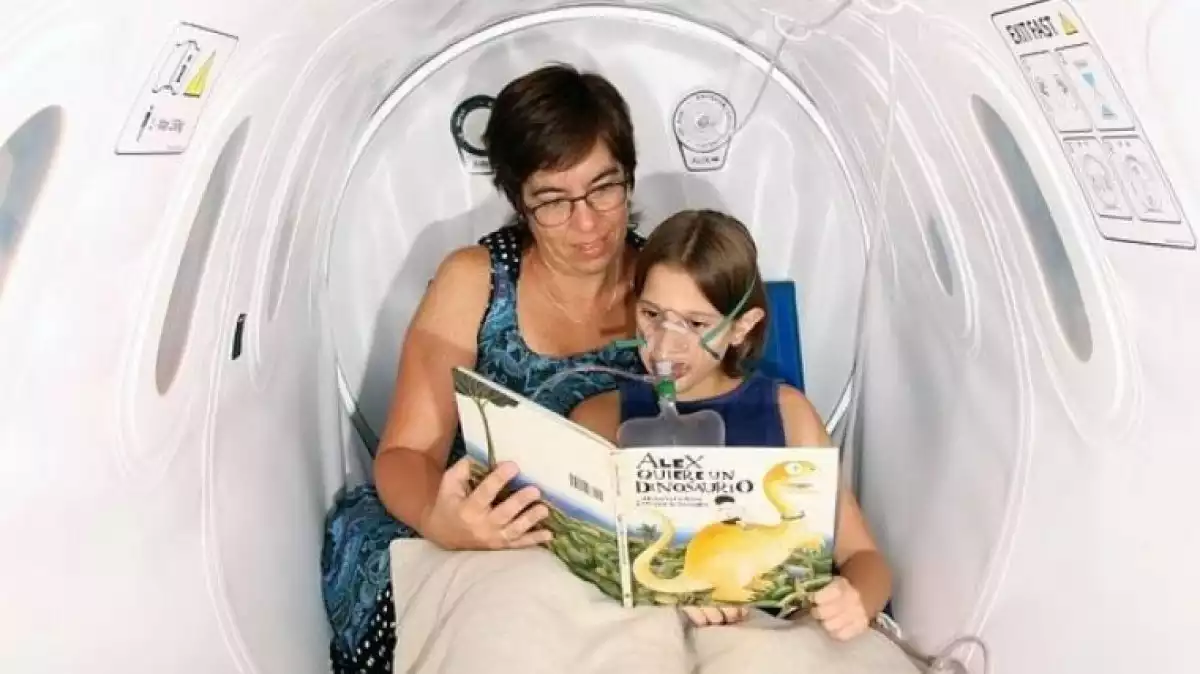

Types of oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy can be applied using different types of oxygen supply systems or devices. In the hospital, for example, oxygen is delivered through a nasal cannula or mask attached to a tube connected to a central source on the wall. However, there are also other devices that can be used at home or away from home, such as compressors, portable oxygen tanks, etc.
Below, we will review some of the most common oxygen supply systems today. These include compressed oxygen, liquid oxygen, oxygen concentrator, and an oxygen conserving device.
1. Compressed oxygen
In this case, the air is stored as a gas in a tank. A flow meter and regulator are connected to the oxygen tank to adjust the amount of oxygen supplied. This device is usually prescribed when oxygen is not continuously needed (for example, when physical activity is performed).
2. Liquid oxygen
This system is also a portable oxygen tank that can be filled from the stationary tank if you need to travel. It is known by this name because oxygen is liquid at very low temperatures. When heated, the liquid oxygen is turned into gas, which is what the person uses.
3. Oxygen concentrator
This way of electric supply is the size of a big suitcase. This device removes part of the air in the room and separates the oxygen, which the person will breathe through a nasal cannula. This system is usually prescribed for patients who require constant supplemental oxygen or who must use it while sleeping.
4. Oxygen conserving device
The oxygen conserving device consists of an inspiratory flow system on demand or pulsed dose. The system uses a sensor to detect when a person begins to breathe in, which is when oxygen is provided. This form of oxygen supply can be used by compressed or liquid oxygen systems, but they are not recommended for everyone.
References
Boleyn, M., & Costello, A. M. (2004). Oxygen Therapy. In A. J. Senagore (Ed.), The Gale Encyclopedia of Surgery (Vol. 2, pp. 1072-1077). Detroit: Gale.
Cooper, A., & Frey, R. J. (2005). Oxygen/Ozone Therapy. In J. L. Longe (Ed.), The Gale Encyclopedia of Alternative Medicine (2nd ed., Vol. 3, pp. 1524-1526). Detroit: Gale.