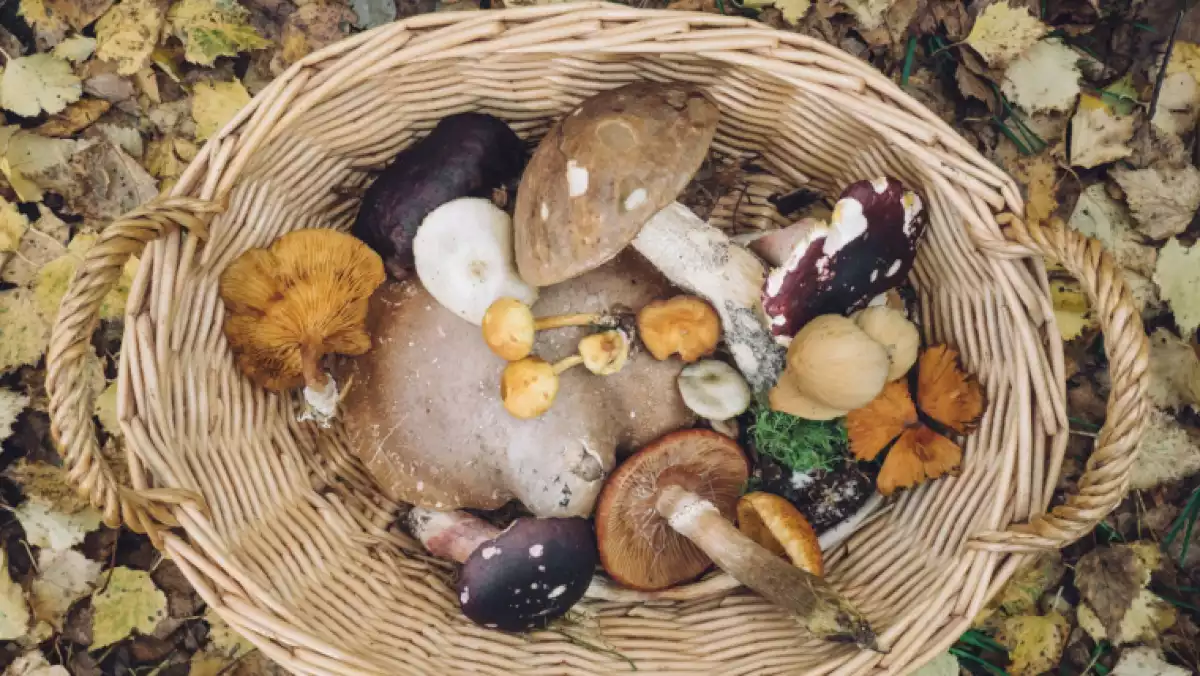
Fungi play a key role in the process of ecological production and decomposition, but they can also be harmful, especially when they grow on the skin. This article will explain what fungi are and their most common types as well as the main fungal infections and their treatments.
What are fungi?
Fungi are neither animals nor plants. The kingdom fungi is composed of a group of microscopic eukaryotic organisms (that is, of eukaryotic cells) which appear in the process of decay.
Fungi are known as the major decomposers of dead matter, which means that they are a kind of natural recyclers which help create antibiotics, decontaminate surfaces or eliminate pests, among other things.
For example, they are used to prepare food and drinks: yeast is a type of single-celled fungus that is used in the fermentation of beer and for making bread rise.
The most common fungi are those growing in soil but there are also in trees, plant leaves and even on the water’s surface. They usually live in decaying matter.
Although fungi and mushrooms are often thought to be the same, mushrooms are actually the outer part of a type of fungus. There are more than 80,000 species of fungi assessed so far, and many more are believed to be discovered. The branch of biology that studies fungi is known as mycology.
Main characteristics of fungi
Fungi are composed of eukaryotic cells, that is to say, they have a cytoplasm, a cell nucleus containing DNA. In fact, this is the difference between fungi and bacteria: the latter are composed of prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus and whose DNA is scattered through the cytoplasm.
In order to reproduce, fungi release spores, which are microscopic cells resistant to high temperatures and humidity. These spores, in both fungi and bacteria, play a protective role.
Unlike plants, fungi do not have chlorophyll, the green substance which is essential in photosynthesis. They feed on decomposing organic matter and the substances released during the process of decomposition. Fungi can be unicellular and also filamentous, as if it were lint.
Types of fungi
Scientific research has provided many ways to classify fungi. It can be done according to their kingdom, species or family, their type of reproduction, their way of feeding, the characteristics of their cells or their functions in the ecosystem, among many others characteristics.
One of the most useful ways to classify fungi is according to their use. Thus, there are edible, medicinal, hallucinogenic (also known as psychoactive), or ornamental mushrooms and parasitic fungi. Let’s have a look at the main characteristics of each one of these types.
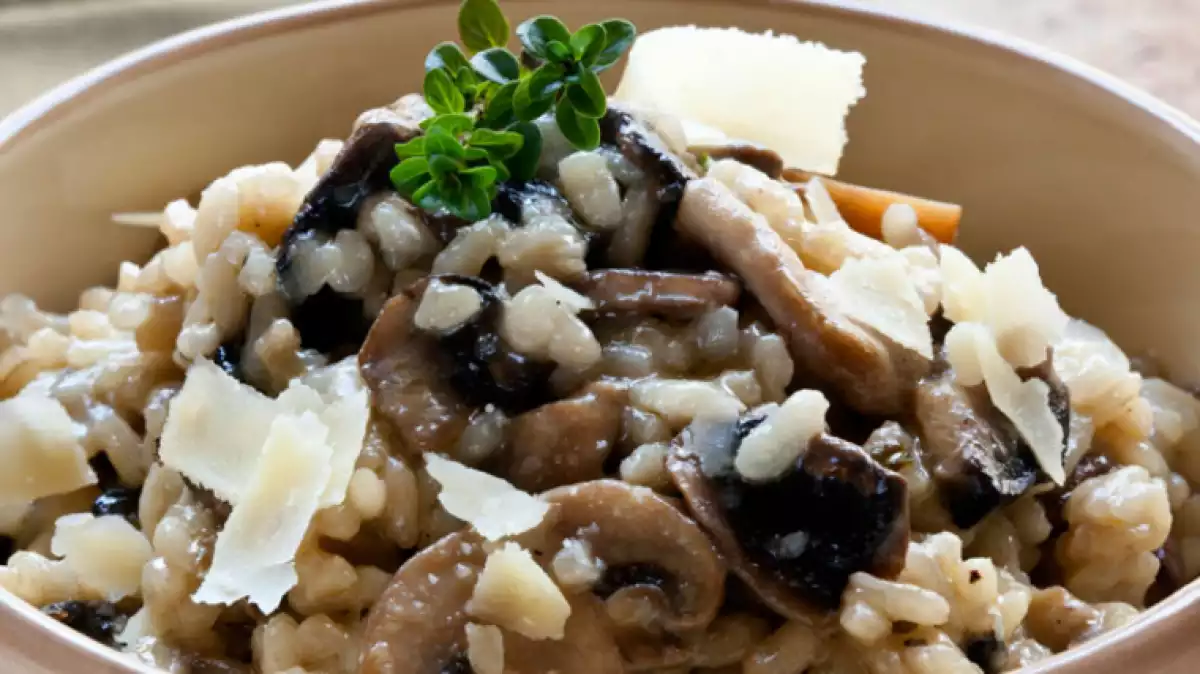

1. Edible mushrooms
These fungi are not toxic or poisonous and have many properties that help you keep a balanced diet. They are low in calories and contain proteins, vitamin B and vitamin D2.
Some of these edible fungi are yeast, truffles and some mushrooms. In México, for example, it is very common to eat corn smut, which is known as "huitlacoche", whereas, in Spain, mushrooms or milk-caps are very popular.
2. Medicinal fungi
Medicinal fungi have experienced a great boom in the last few years, due to the revival of traditional and organic medicine used for the treatment of diseases. An example of a fungus with medicinal properties is Trametes versicolor, also known as turkey tail.
This type of fungus has been used in the treatment of cancer and to improve the functioning of the immune system. However, its effects are still being scientifically investigated.
3. Hallucinogenic mushrooms
Hallucinogenic or psychoactive fungi have been a part of the development of our civilization, since they have been used to create mystical experiences in ancient rites that seek physical and mental healing, as well as being used as recreational drugs.
There are more than 190 species of hallucinogenic fungi known all over the world. They are even being used in the treatment of some mental disorders.
4. Ornamental mushrooms
Ornamental fungi are used to decorate. For example, they have been used in ceremonial rites and as offerings or gifts, instead of flowers, by some ethnic groups from central-southern Mexico.
5. Parasitic fungi
Parasitic fungi have toxic effects that cause infections and may be found in the human body, for example. Due to their dermatological effects, these are known as dermatophytes. They damage the skin tissue, which causes infections, some of them contagious.
Parasitic fungi can also cause agricultural pests, which have been linked to the excessive use of chemicals. Therefore, some of the agricultural methods have had to be changed.
Fungal infections and their treatments
As mentioned before, fungi can grow in soil and are very resistant to humid environments. That is why fungal infections of the feet are one of the most common, but they are not the only ones. They can also be found on the hands or genitals.
Fungal infections are not hereditary, but they are contagious. Generally speaking, fungal infections can be prevented by practicing good hygiene habits and strengthening the immune system.
Once the infection has appeared, you can find various treatments, from homemade remedies with fruits and minerals to dermatological ointments.
Fungal infections are also known as candidiasis when they are caused by a yeast fungus of the Candida species, which grows in the mucous membrane and the skin.
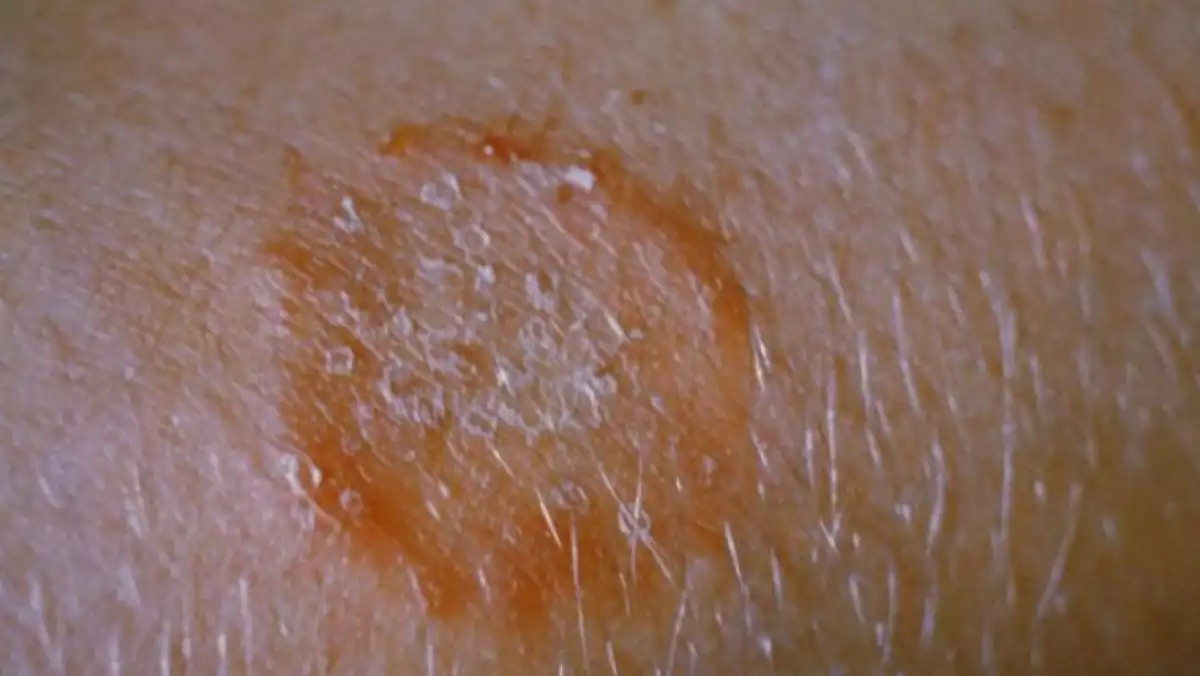
1. Fungus on feet
The fungi that appear on feet cause cracks, pain, burning or itching, irritation, unpleasant odour and even blisters. They can spread from your toes to the soles or nails of your feet. The most common infection is known as athlete’s foot, which is caused by sweating and its contact with your socks.
There are many home remedies that can help you get rid of fungi, since they regulate the pH, as well as the irritation and the degree of dryness of your skin. The most common remedies include white vinegar, baking soda, pineapple, lemon, and salt baths. There are also ointments or creams that can cure them, which are known as antifungal creams, such as Miconazole.
2. Fungus on nails
This type of fungal infection is also known as “onychomycosis”. It usually appears on the fingers and spreads around the area. The most common is the fungal infection of the toenails, which is caused by the athlete’s foot, but it can also be caused by wearing tight shoes over a long period of time.
Fungi can also grow on hands. One of the factors that triggers them is biting your nails, using artificial nails, excessive sweating, or keeping your hands in water for a long time.
The fungal nail infection is very contagious, so it is recommended to be careful when sharing showers and personal items such as nail clippers.
3. Oral thrush
This type of fungi is rare and causes pain when talking and eating, as well as bleeding when brushing your teeth, gum swelling, white patches inside your mouth and on your tongue, irritation, itching and cracks in the corner of your mouth.
They are associated with diseases caused by a weak immune system, a high blood sugar level, malnutrition and constant consumption of tobacco or alcohol.
This fungal infection is also common in very young children who have not yet developed the oral flora. It can be caused by dry mouth and low pH, and by the use of dentures that is not combined with a good hygiene. There are special medications for oral thrush, for example Nystatin.
4. Vaginal thrush
Vaginal candidiasis is a very common infection. It is estimated to be experienced by all women at least once in their lifetime. The symptoms are: white and thick vaginal discharge, which is odourless, as well as itching, irritation, burning and redness around the vagina. There may also be pain during urination.
Among the most frequent causes, there are: the use of tight underwear that leads to heat and moisture, or pregnancy, as well as the use of contraceptives, steroids or antibiotics, since this type of drugs can kill the natural bacteria that slow down the growth of yeast.
Pharmacy treatments include suppositories, vaginal creams and pessaries for thrush. For complicated infections, it is necessary to consult a specialist who can perform an examination by taking a sample of whitish secretion in order to determine the most appropriate treatment.
In order to prevent vaginal thrush, you should wear cotton underwear, avoid douching, and not use wet or damp suits for a long period of time. It is also recommended to avoid using tampons during infection.
Check out the original article: ¿Qué son los hongos? Los 9 tipos principales y sus características at viviendolasalud.com
