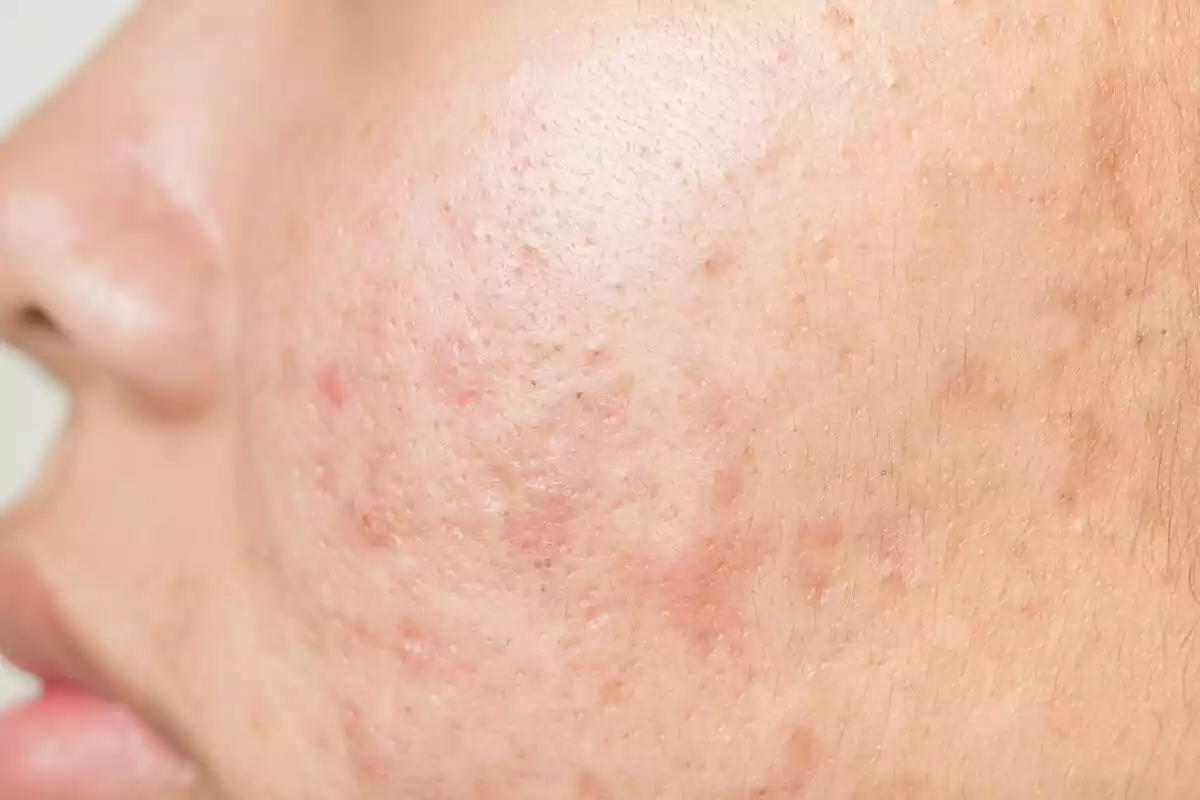
During adolescence, acne can be hard to deal with since it affects a person’s physical appearance. Acne causes low self-esteem, emotional issues, and a number of related problems for the people that suffer from it, especially in severe cases.
Early treatment is critical since symptoms can be controlled and scarring avoided, which otherwise could last into adulthood.
In this article, we will explain what acne is, its causes, and the main types found in adolescents. Also, we will tell you how to get rid of acne and the marks that it leaves through the effective medical treatments that we currently have access to.
What is acne?
Acne is a skin condition that leads to “pimple” or “blackhead” breakouts in different parts of the body, especially the face, chest, and back.
The most common form of this skin condition is juvenile acne, hormonal acne, or acne vulgaris -the kind that affects adolescents and young adults. Hormonal acne tends to be more severe in men but, it still also affects many women and can last into adulthood.
As far as its symptoms, acne itself is not visible, generally speaking, but the wounds that provoke it are. These can cause physical signs like swelling, pain, itchiness, and inflammation.
During puberty and adulthood, the androgen levels in the hormones increase. This increase causes an excess of sebum in the person's body, and when combined with dead cells and some of our skin’s bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), this causes acne.
Keep in mind that acne scars appear when new skin cells form to replace the ones damaged during the process that we have described.
Causes
Although before it was believed that acne was caused by certain foods (chocolate, fatty meat…) and a person’s hygiene habits, today it is known that there are different factors involved in its appearance. Among these, the following stand out:
- Being an adolescent or young adult
- Being a man
- Hormonal disorders in girls/women
- Hormonal changes (menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause)
- Diet (No food causes acne, but some can cause breakouts)
- Medications (acne can be a side effect of pharmaceuticals like antidepressants, antibiotics, or contraceptives)
- Cosmetics (makeup sprays)
- Environment (exposure to polluted air, excessive sweating…)
- Emotional stress (can contribute to its development due to the physiological hyperactivity that this implies)

Types: inflammatory and comedone
There are two main types of hormonal acne: inflammatory and comedone. Inflammatory acne is the most severe variety, especially because of the nodules and cysts that this causes.
Comedonal acne is the formation of blackheads and pimples on the skin’s surface, however, acne belongs to the inflammatory variety when a pimple causes the rupture of the follicle wall.
Inflammatory acne presents itself in the form of papules (red lumps sensitive to the touch), pustules (pussy lesions), nodules (large lesions, painful and deep), and cysts (puss filled lesions deep in the skin that can cause scarring).
Treatment
There is no cure for acne, but it can be controlled with proper treatment. Improvements can be seen after two or more months and usually after treatment is stopped. Even so, sometimes it improves over time suddenly, generally after adolescence.
Inflammatory acne can leave scars that require additional treatment. Breakouts can be minimized by gently washing affected areas, avoiding abrasive cleansers, using noncomedogenic makeup, washing hair often and keeping it off of your face, sticking to a balanced diet, and not popping pimples and blackheads (without going to a specialist).
Acne treatment involves reducing the amount of sebum, getting rid of dead cells, and killing bacteria with either oral or topical medication. The method chosen depends on how severe the condition is.
Topical medication
Topical medications are available in cream, gel, or lotion form. These include antibiotics like erythromycin, clindamycin (Cleocin T), and meclocycline (Meclan), comedolytics (ingredients that loosen clogged pores) like vitamin A, retinoic acid (Retin-A), salicylic acid, adapalene (Differin), resorcinol and sulfur, or a combination, like azelaic acid (Azelex), or Benzoyl peroxide plus erythromycin (Benzamycin).
The possible side effects of this kind of pharmaceutical include mild redness, peeling, irritation, dryness, and increased sensitivity to sunlight.
Oral medication
Oral antibiotics need to be taken daily for 2-4 months. The medications that are used include tetracycline, minocycline (Minocin), doxycycline, clindamycin (Cleocin), and Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra).
The possible side effects include allergic reactions, upset stomach, vaginal candidiasis, dizziness, and tooth discoloration.
Oral isotretinoin (Roaccutane or Accutane) is a medication used in severe cases of acne. This is the treatment of choice for those with severe cystic acne and nodules and is used with or without topical or oral antibiotics. This treatment tends to last between 4 and 5 months and is highly effective.
However, this medication often has adverse effects like temporary exacerbation of the acne, dry skin, nasal hemorrhages, vision disorders, and elevated liver enzyme and cholesterol levels, among others.
How to get rid of acne scars
Various surgical procedures or medications are available to reduce acne or scarring. A few examples of these include blackhead extraction, chemical peels, dermabrasion, “punch grafting,” intralesional injection, and collagen injection.
References
McLaughlin, M. (2002). Acne. In D. S. Blanchfield & J. L. Longe (Eds.), The Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine (2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 24-27). Detroit: Gale.
Powers, J. L. (2004). Acne Medication. In J. J. Lagowski (Ed.), Chemistry: Foundations and Applications (Vol. 1, pp. 12-15). New York: Macmillan Reference USA.