In addition to being a beautiful flower, dandelion is one of the most recognized plants for its health benefits, even though many people don't know them. In this article we will talk about this plant and its uses.
What is dandelion?
Scientifically known as Taraxacum, dandelion is a species of flower belonging to the Asteraceae family. It is believed to be a type of plant originating in certain regions of Europe and North America and appeared approximately 30 million years ago in Eurasia.
It is a kind of herbaceous and perennial plant that grows and develops very easily in temperate climates. Also, they are highly appreciated by farmers because they grow quickly and effectively.
Although this plant has a large number of properties, these are not popularly known. Therefore, it is traditionally used as an ornamental plant due to its beautiful flowers. This plant has two different types of flowers, depending on the subspecies. Both are fully edible, but all are characterized by having bright yellow flowers.
In traditional medicine, dandelion has been widely used in the treatment of stomach conditions, intestinal gas, joint pain, eczema and rashes or certain types of infections, especially viral ones.
Also, this plant is fully edible so it is highly appreciated as a culinary ingredient. Some of the most common dandelion recipes are salads, soups, wines and teas. In many places, they substitute coffee by the roasted root of this plant.
Dandelion benefits
Traditional medicine has used this plant in the treatment of an infinite number of physical conditions. However, not all of them have been supported by scientific evidence. Currently, laboratory studies try to determine how to use the different properties of this plant to treat all kinds of physical pathologies more naturally.

Among the main uses and benefits of dandelion are:
1. Improves bones health
This plant is rich in calcium, which is a basic mineral in the development and strengthening of bones. Also, it is also rich in vitamin C and luteolin, two antioxidants that protect bones from age-related deterioration, which is mostly due to the effect of free radicals.
2. Treatment for liver diseases
Dandelion extract is traditionally known for its liver benefits. The antioxidants mentioned above promote the proper functioning of the liver and protect it against aging. Moreover, there are other compounds in this plant that can be effective in the treatment of liver hemorrhages.
A dietary supplement can help maintain a proper bile flow while stimulating liver function and aiding digestion. Adequate digestion reduces the risk of constipation and severe gastrointestinal problems.
3. Helps control diabetes
It has been proven that dandelion juice can stimulate insulin production in diabetic people, thus maintaining low blood sugar levels.
Besides, thanks to its diuretic properties, it increases the need to urinate in diabetic patients, which helps to eliminate excess sugar from the body.
4. Treatment for skin conditions
The sap extracted from dandelion is a natural and effective treatment for skin conditions caused by bacterial and fungal infections. The reason is that the sap of this plant has alkaline properties, germicides, insecticides and fungicides.
It is important that sap is not in contact with the eyes. It can be applied in eczemas and for itching, and it doesn't have side effects.
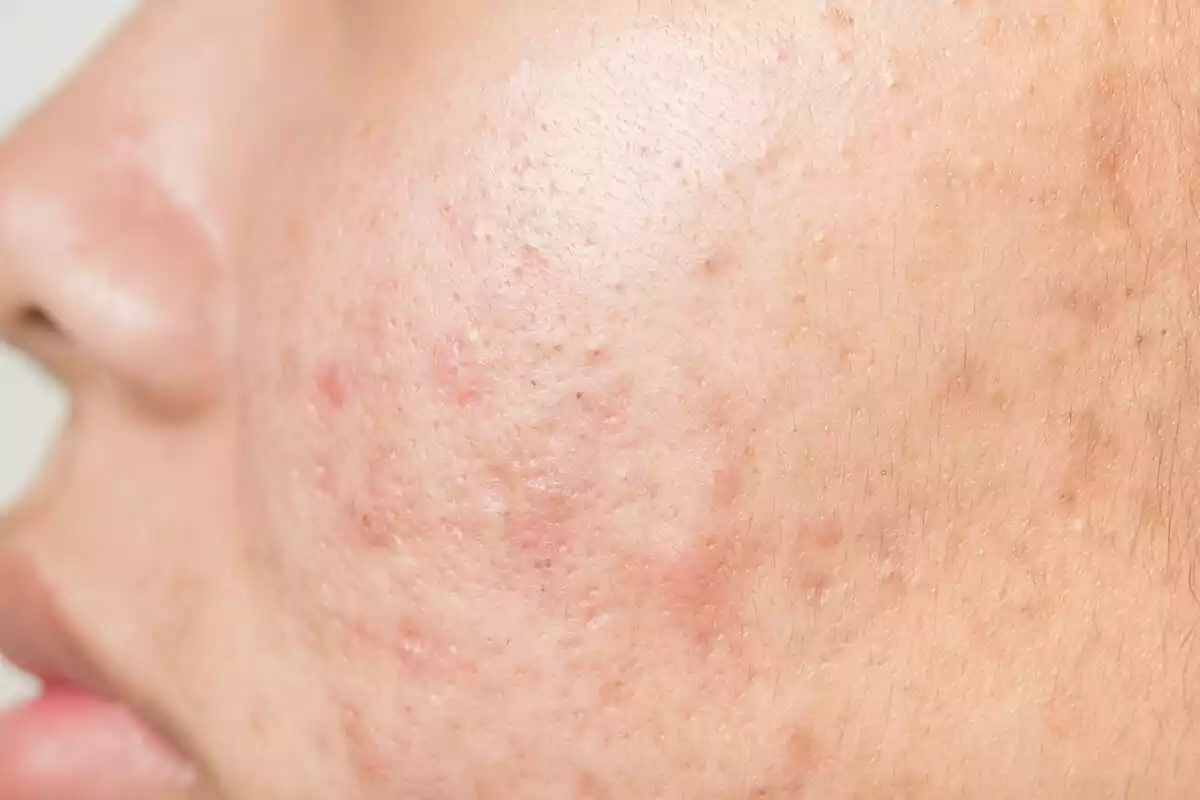
5. Acne prevention and treatment
Along with its diuretic properties, dandelion is a powerful detoxifier, stimulant and antioxidant, making it an effective treatment for acne, especially that caused by hormonal alterations.
Its extract can promote hormonal regulation and balance, increase sweating and promote the opening of pores. All this helps to facilitate the expulsion of toxins through sweat and urine. Besides, applying the sap of this flower to the skin can inhibit microbial infections and reduce the signs of acne.
6. Helps liquid retention
This plant promotes urination and helps eliminate excess water from our body. Also, our urine contains a percentage of 4% fat, so the more we urinate, the more water and fat we lose, so it also promotes weight loss.
7. Constipation treatment
High fiber contents make it very beneficial for proper digestion and intestinal health. The fiber stimulates bowel movement and reduces the chances of constipation and diarrhea.
8. Prevents anemia
Dandelion has high levels of iron, vitamins and protein. While iron is an essential part of blood hemoglobin, vitamin B and proteins are the basis for the formation of red blood cells and other blood components. Therefore, it may help anemic people keep this condition regulated and under control.
9. Regulates blood pressure
Urination is an effective way to reduce blood pressure. Dandelion juice increases urination both in quantity and frequency, thus helping to lower high blood pressure.
Also, fiber is useful for lowering cholesterol and therefore helps lower blood pressure, as cholesterol is one of the factors that increase blood pressure.
References
Menghini, L., Genovese, S., Epifano, F., Tirillini, B., Ferrante, C. & Leporini, L. (2010) Antiproliferative, protective and antioxidant effects of artichoke, dandelion, turmeric and rosemary extracts and their formulation. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology, 23(2): 601-610.
Schütz, K., Reinhold, C. & Schieber, A. (2006). Taraxacum—a review on its phytochemical and pharmacological profile. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 107(3): 313–323.
