The penis is the most important organ in the male reproductive system, at least from a social standpoint. There are many techniques that promise to enlarge the penis, although many of them have yet to be proven effective.
While all penises have the same structure and functions, they are not all similar when it comes to size and shape.
We will discover what the penis is, what structure and functions it has, as well as what types of penises there are. Finally, we will examine possible penis enlargement methods and find out which are the most popular.
What is the penis?
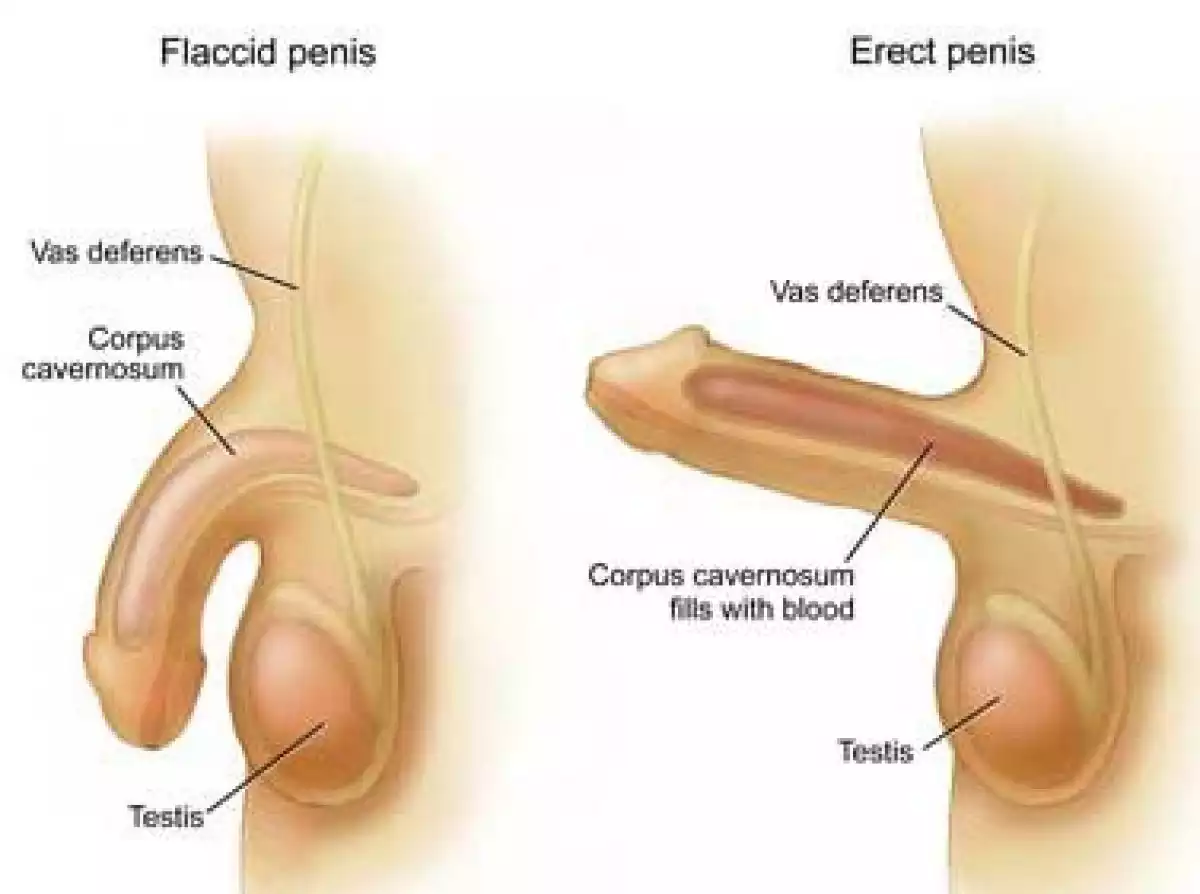
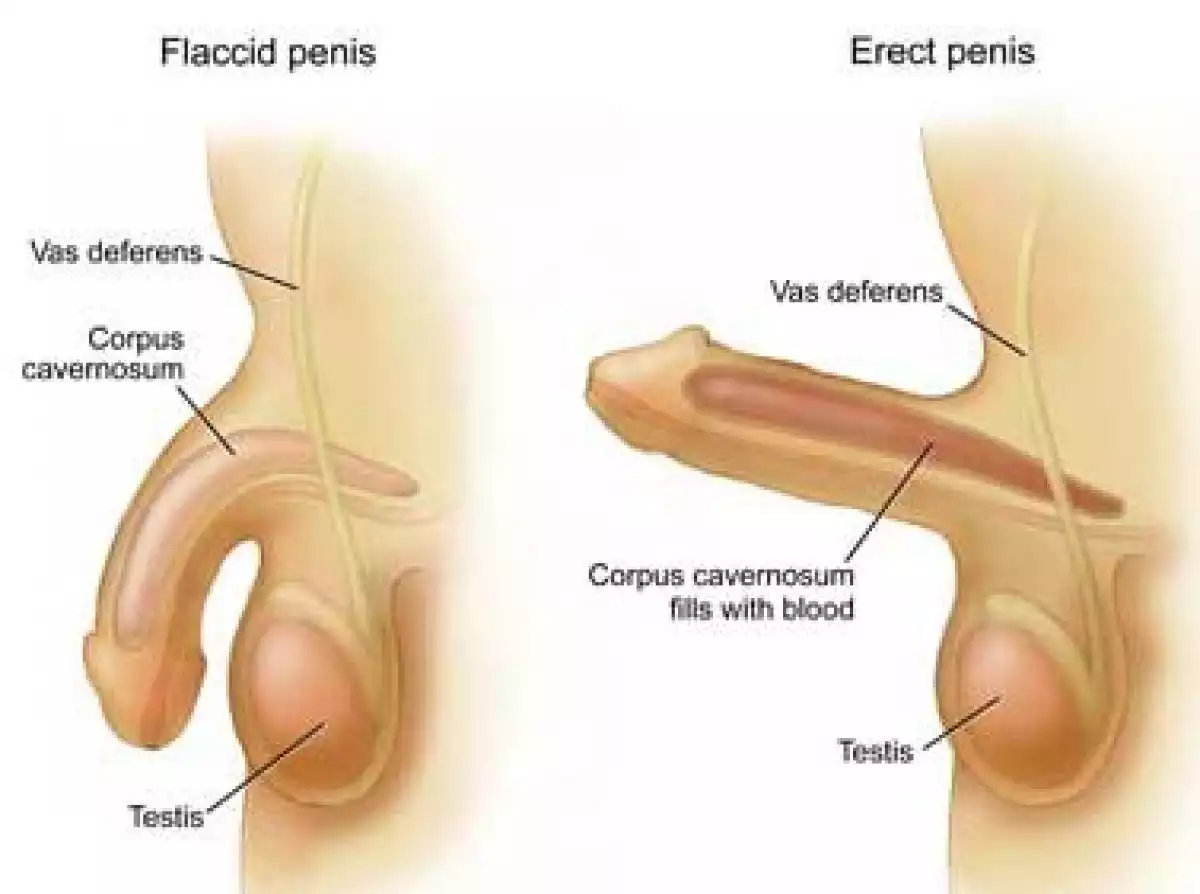
The penis is the male sex organ, reaching its full size during puberty. In addition to its sexual function, the penis acts as a conduit for urine to leave the body as well as semen during ejaculation. Normally in a flaccid state, the penis will become erect once sexually aroused.
Erection is a physiological phenomenon in which the penis becomes firm, engorged, and enlarged which facilitates coitus. When despite sexual stimuli, the penis does not become erect it could mean a possible erectile dysfunction, which has various causes ranging from psychological to physiological.
Finally, ejaculation occurs when the man reaches climax and ejaculates the semen. This could be a result of oral sex, intercourse - either vaginal or anal or masturbation. In the practice of tantric sex, the orgasm can be delayed or happen without ejaculation. This is also known as a dry orgasm.
Average penis size
The average penis size varies around the world between 12 and 16 centimeters while erect.
It's interesting to mention that there are great variations of size when it comes to the flaccid penis.
So, what is the biggest penis ever measured? According to the Guinness Book of Records, that record is held by a Mexican man with a 48-centimeter penis, and on the second place, an American actor and writer with a 34-centimeter penis.
Penis structure and functions
The penis is an organ from the male reproductory system and it is made up of different parts which fulfill a specific function.
The human penis is made up of three pillars:
two corpus cavernosum which are placed on either side of the penis
corpus spongiosum, placed on the inferior side of the penis
The arteries that supply the blood for erection enter the corpora cavernosa ( plural) and produce the erection.
The structure of the external male reproductive system is comprised of five main elements described below.
1.Glans
The glans represent a bulbous tissue that is known as the head of the penis, seeing how it is located at the end of the organ. It is highly vascularized and contains many nerve ending which is why it is the most sensitive part of the penis.
The urethral opening can be found at the tip of the glans and it provides an exit for urine as well as semen during ejaculation.
2. Foreskin (prepuce)
The foreskin is a type of elastic skin that covers and protects the male reproductive organ in its flaccid state. During erection, the foreskin retracts and exposes the glans. Circumcised men do not have a foreskin as it is surgically removed.
3. Scrotum
The scrotum is a sac of skin that hangs just below the penis and contains the testicles. The temperature in the scrotum tends to be around 2ºC or 3 ºC lower than body temperature in order for sperm to be produced effectively.
4. Frenum
The frenum is an elastic band of tissue under the glans that connects to the foreskin and presents a slightly V-shaped notch. This tends to be an extremely sensitive part of the genital system that could tear during intercourse.
5. Corpus spongiosum
The corpus spongiosum extends from the tip of the glands and down into the abdomen and it contains the urethra. There are different shapes of corpus spongiosum, both straight and curved.

Types of penises - Size and shape
Similarly with the female genital system, there are many types of male genitals with different sizes and shapes. Each of them has a special feature which can improve or hinder sexual performance, although it is not always the case.
We will have a look at the eight most common types of penises.
1. Circumcised penis
In this case, the main trait is that the foreskin (the skin that protects the glans) has been surgically removed. According to the World Health Organization, 33% of adult males worldwide are circumcised.
An important feature to remember is that circumcised penises tend to be more sensitive in the beginning and then gradually lose sensitivity which is why glans stimulation is important.
2. Uncircumcised penis
The difference from the previous example is that the uncircumcised penis has the foreskin intact. When the penis becomes erect, the prepuce is stretched and stimulation can be easily achieved by raising and lowering this skin.
3. Curved or bent penis
This type of penis has a curved shape, either to one side or the other and the general consensus is that it's an ideal shape to stimulate the female G spot. If the curvature is too extreme, however, it can lead to painful intercourse.
A bent penis could also be a sign of Peyronie's disease (fibrous scar tissue inside the penis that causes curved, painful erections).
4. Micropenis
Micropenis is a medical term for a penis, usually diagnosed at birth, that is well under the normal size range. The measurement while in a flaccid state is of 2 centimeters while in erection, it's less than 7 centimeters.
If diagnosed correctly, there are methods that help manage this condition such as testosterone treatments.
5. Thick penis
The size of the male penis is not only determined by the length but also by the birth of the organ. A penis classifies as being thick if it surpasses 4-5 centimeters.
Just like any other characteristic, if used correctly, it could result in pleasant intercourse.
6. Big penis
One does not have to possess a 48 centimeters member to be a part of this category. In reality, anything more than 16 or 17 centimeters is considered a big penis.
This type of penis, however, could cause problems during intercourse, but with adequate lubrication, exercises, and the correct postures, it shouldn't pose much of a risk.
7. Small penis
Its size tends to be between 8 and 11 centimeters while erect. There are, however, certain penises that when flaccid may appear smaller than they actually are.
Although the general assumption is that size matters, sexual pleasure is not determined by the size of the penis, and a smaller organ could be just as effective as a bigger one.
8. Average penis
In this case, we are discussing the average-sized penis that doesn't change its size too much either when flaccid or erect. As mentioned earlier, the average penis size tends to be around 12-16 centimeters.

How to make your penis bigger?
Penis enlargement represents an important social and cultural concern for many individuals. Social pressure that equates penis size with masculinity is a controversial topic in Western societies.
Many men have reported mental health problems associated with these expectations which is why nowadays, there are several medical devices available on the market that satisfy this demand. We have compiled a list of 5 of the most popular penile enlargement methods.
1. Penis enlargement exercises
Stretching exercises are non-invasive methods that have gained quite a lot of popularity. One of the most practiced methods is jelqing- the thumb and index finger are wrapped around the penis and repeatedly drawn away from the body in order to force blood into the glans and encourage vascularity.
There are no conclusive studies to show the effectiveness of this method and side effects such as pain, irritation, scar formation, and blood vessel tears could happen due to incorrect jelqing.
2. Penis extender
Introduces the use of various devices, such as stretchers and penis pumps. Similarly to the enlargement exercises or massages, penis extenders lack scientific validation. The stretchers, however, have been found useful in enlarging the penis while flaccid, however, no changes were recorded in the erect size.
3. Non-invasive enlargement methods
By simply changing the aesthetics of the pubic area, one can create the optical illusion of having a bigger penis. Shaving the pubic hair and dieting to reduce the amount of fat in the area are useful strategies in achieving a larger look.
Penis piercing could also fall into this category of non-invasive methods of penis enlargement, especially because it could produce more pleasure. It is important to see a professional piercer and follow all the aftercare instruction they give you.
4. Phytotherapy
The key is consuming vitamins and minerals that according to phytotherapy can favor vasodilation of the corpora cavernosa, increase testosterone production, and encourage stretching, among others. This practice and its results have yet to be scientifically proven, much like the rest of other penis enlargement techniques.
5. Surgery
Penile enlargement surgery can be performed with the intention to change the length or the girth of the penis. It is known as penile plastic surgery and it is recommended to a limited number of people especially those diagnosed with micropenis.
Anyone else interested in this procedure should have a psychological assessment done prior to the intervention. Studies have shown that 96% of the men who intend on getting penile plastic surgery end up changing their mind due to the abundance of possible psychological damage and physiological side effects.
- This article about "The Penis" was originally published in Spanish in Viviendo La Salud
References:
Aaronson, I. A. (1994). Micropenis: medical and surgical implications. Journal of Urology, 152: 4-14.
Alter, G. J. (1998). Penile enlargement surgery. Techniques in urology, 4(2): 70-76.
Bordo, S. (1999). The Male Body: A New Look at Men in Public and in Private. New York: Farrar, Straus, and Giroux.
Dillon, B. E., Chama, N. B., & Honig, S. C. (2008). Penile size and penile enlargement surgery: a review. International journal of impotence research, 20(6): 519.
Guzmán Esquivel, J. (2008). Micropene. Revista Mexicana de Urología, 68(1): 1-2.
Ruffion, A., Azam, P., & Leriche, A. (2004). Cirugía plástica y reparadora del pene. EMC - Urología, 36(1): 1–10. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1761-3310(04)40328-4
Vardi, Y., & Gruenwald, I. (2009). The status of penile enhancement procedures. Current opinion in urology, 16(6): 601-605.